Trimble® eCognition® Suite is an advanced analysis software available for geospatial applications. It is designed to improve, accelerate and automate the interpretation of a variety of geospatial data and enables users to design feature extraction or change detection solutions to transform geospatial data into geo-information.
eCognition imports a variety of geospatial data, fusing them together into a rich stack of geo-data for the analysis. The analysis logic is structured into series of steps to create a computer-based representation of an expert’s geospatial interpretation process a so called Rule Set. eCognition then combines the analysis logic with scalable computing power to identify changes over time or features on the earth’s surface across very large sets of data.
eCognition Suite version 9.5 is a major release and includes a range of new features and bug fixes. We recommend upgrading to this new version to benefit from the new features and improvements. For an overview of the highlights please refer to the chapter Overview. A complete list of new features and bug fixes can be found in chapter New Features - Bug Fixes and Limitations

Building Analysis Solutions
The eCognition technology examines image pixels not in isolation, but in context. It builds up a picture iteratively, recognizing groups of pixels as objects. Just like the human mind, it uses color, shape, texture, shape and size of objects, as well as their context and relationships, to draw the same conclusions that an experienced analyst would draw.
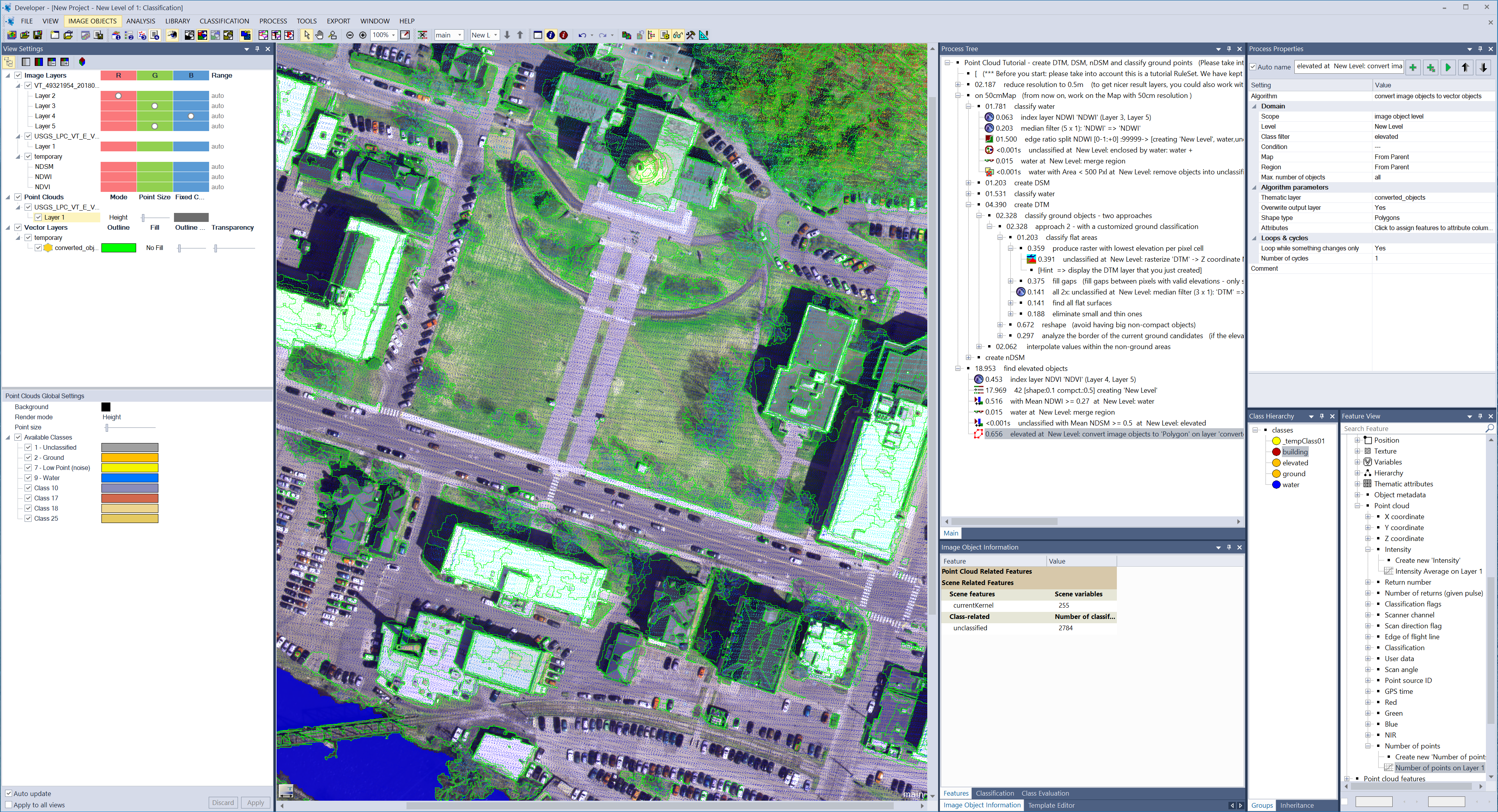
To build an analysis solution, it is possible to flexibly combine the image interpretation steps like object creation (segmentation), object classification (knowledge based, fuzzy logic, machine learning), object detection (template matching) and object modification (fusing, smoothing, orthogonalization, simplification) into a Rule Set or even a new application (Rule Set with UI) to solve the analysis problem.
The result is a unique approach to translate mind models (why a human interpreter can see the objects, changes, or features in the geospatial data) into computer understandable code (Rule Set) or an individual/customized application.

Leveraging Data Synergies
eCognition can fuse a variety of geospatial data, such as spectral image data, 3D structure data from point clouds and spatial/thematic data from GIS vectors.
The proximity of eCognition to GIS, its ability to link and fuse the available data in an analysis - combined with the straightforward export of results to GIS layers - help eCognition users to achieve outstanding results.

Efficient Workflows
The eCognition Suite offers three different components which can be used stand-alone or in combination to solve even the most challenging fully automated and semi-automated production tasks:
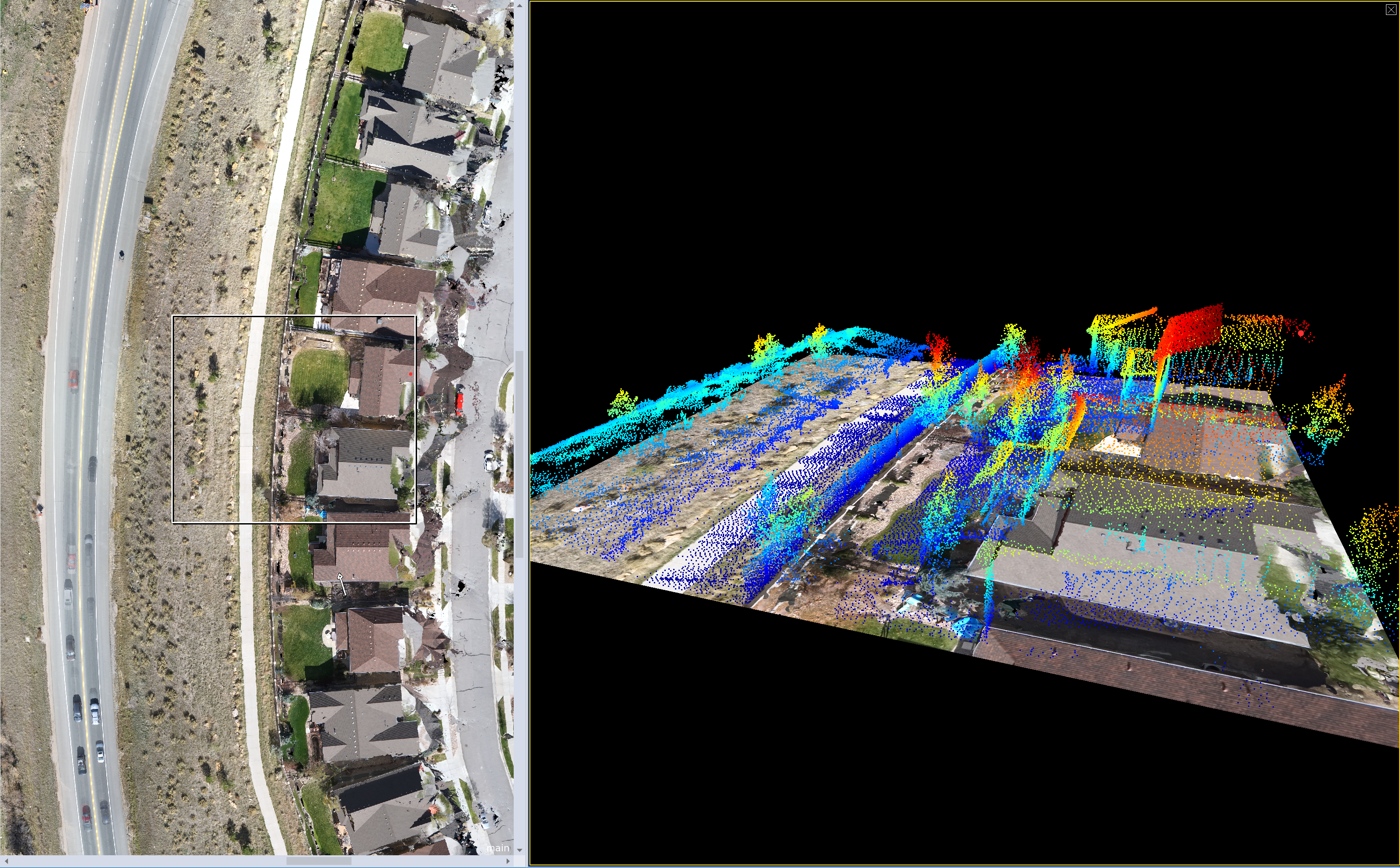
eCognition Developer 9.5 has boosted point cloud operability on two fronts: functionality and processing. A new point cloud resampling algorithm is available to reduce the oversampling of points in dense regions and thus increase processing speed. In addition, raster layers can now be displayed within the 3D viewer to enrich data fusion and aid rule set development.
Deep Learning and convolutional neural network performance continues to improve in version 9.5. eCognition’s Deep Learning algorithms have been expanded to support models using batch normalization leading to speedier and more robust learning. New advanced sample manipulations help automating production workflows.
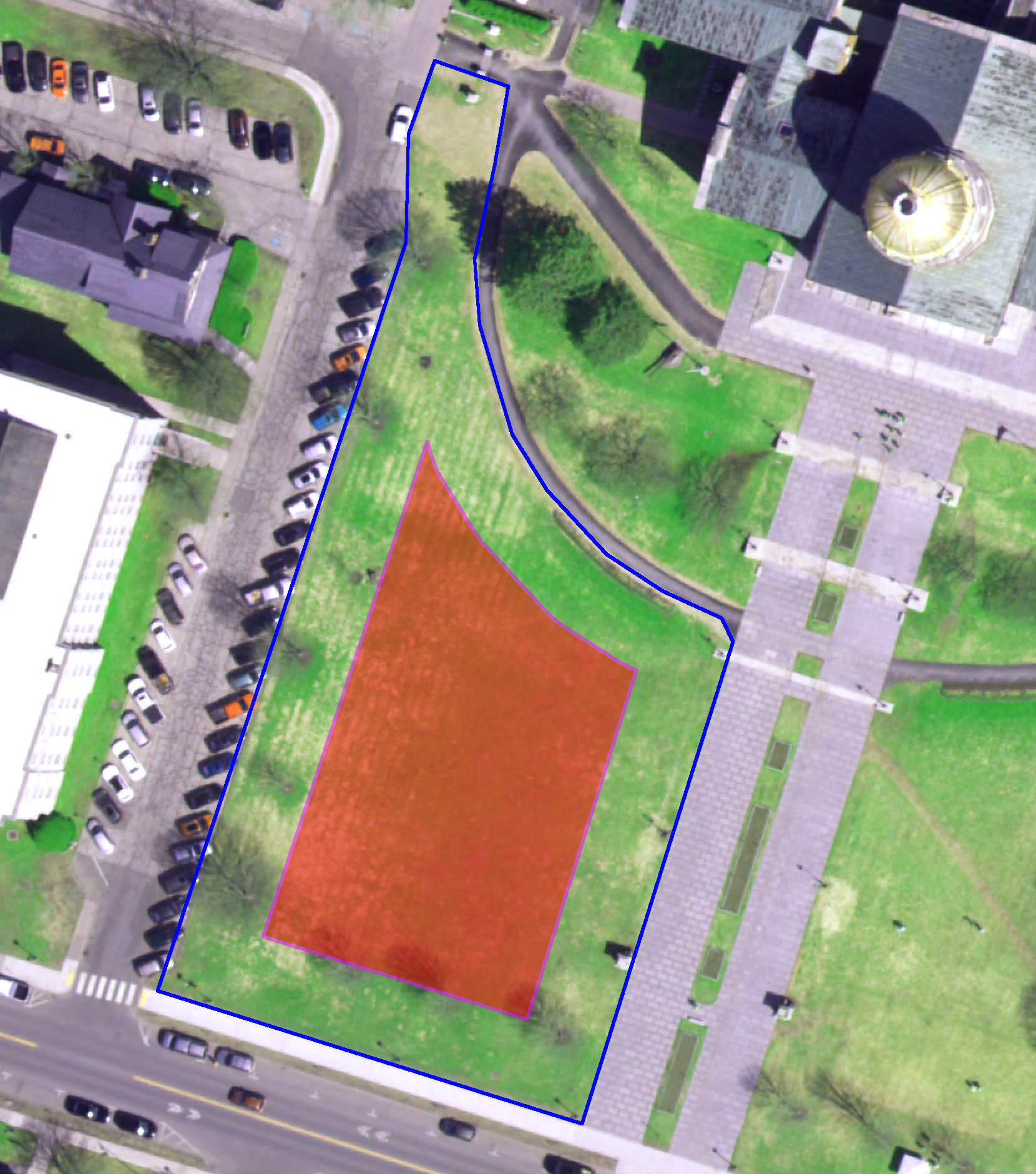
In 9.5, we continue to grow the pallet of vector analysis tools and capabilities. Region support for vector algorithms offers clear performance benefits. Such regions can now be conveniently generated based on vector domains.
Many new features and algorithms allow more flexible processing exclusively based on vector domains. For instance, it is now possible to calculate statistics in the vector domain, to shrink polygon vectors, and to access layer values and object class under point vectors.